Discover the benefits and impact of a monotrophic diet on health. Learn what foods are allowed and how to transition to this healthy eating approach.
What is Monotrophic Diet?
Contents
A monotrophic diet is a type of diet that focuses on the consumption of a single type of food at each meal. This means that during a meal, you only eat one type of food, such as bananas, apples, or spinach. The idea behind this diet is that it simplifies the digestive process by allowing the stomach to focus on breaking down and absorbing nutrients from a single source of food.
Proponents of the monotrophic diet believe that it can lead to improved digestion, increased energy levels, and better overall health. They argue that by eating only one type of food at a time, the body can more easily process and absorb nutrients, leading to better digestion and fewer digestive issues.
However, critics of the diet argue that it may not provide all the necessary nutrients for a balanced and healthy diet. They suggest that eating a variety of foods is important for getting all the essential vitamins and minerals that the body needs to function properly. Additionally, they point out that sticking to a monotrophic diet may lead to boredom and ultimately make it harder to stick to the diet in the long run.
Overall, the monotrophic diet is an eating plan that focuses on consuming a single type of food at each meal. While some people believe that it can lead to improved digestion and overall health, others are skeptical of its long-term effectiveness and its ability to provide all the necessary nutrients for a balanced diet.
Benefits of Monotrophic Diet
The benefits of monotrophic diet are numerous and can have a significant impact on your overall health. This type of diet focuses on eating only one type of food at a time, which can help to simplify your meals and make it easier to digest. By focusing on one food group at a time, you can also better identify any food sensitivities or allergies you may have, leading to improved digestive health and reduced inflammation.
Another benefit of a monotrophic diet is that it can lead to better portion control. By eating only one type of food at each meal, you are less likely to overeat and can better tune into your body’s hunger and fullness cues. This can help to prevent weight gain and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Additionally, a monotrophic diet can provide a sense of mental clarity and focus. By simplifying your diet and reducing the variety of foods you eat, your body can more easily digest and absorb nutrients, leading to improved energy levels and cognitive function.
Some individuals also report improved skin health and reduced acne when following a monotrophic diet, as it can help to eliminate potential triggers for skin issues, such as dairy or processed foods. Overall, the benefits of a monotrophic diet may include improved digestive health, better portion control, mental clarity, and potential improvements in skin health.
Foods Allowed on Monotrophic Diet
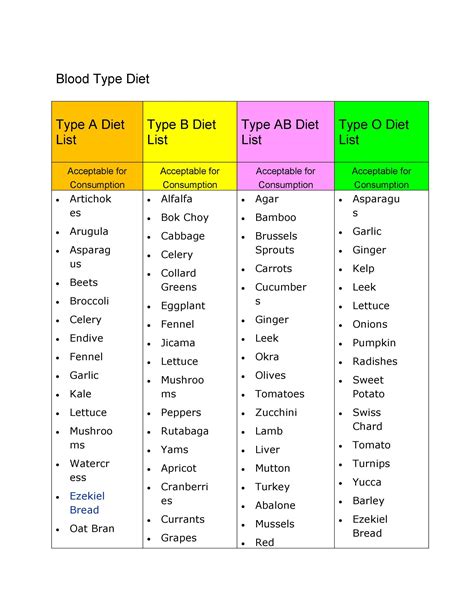
When following a monotrophic diet, it is important to know which foods are allowed and which are not. This diet focuses on consuming only one type of food at each meal, which means that the options for allowed foods are limited. The main foods allowed on a monotrophic diet include:
Fruits: Most fruits are allowed on a monotrophic diet, including bananas, apples, berries, and citrus fruits. These can be consumed either individually or as part of a fruit salad.
Vegetables: Some vegetables, such as cucumbers, tomatoes, and bell peppers, are also permitted on a monotrophic diet. These can be eaten raw or cooked, depending on personal preference.
Grains: Certain grains, such as rice and quinoa, may be included in a monotrophic diet, but they should be eaten separately from other food groups.
Nuts and Seeds: Some monotrophic diets allow for the consumption of nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds, as long as they are not combined with other foods.
Impact of Monotrophic Diet on Health
Switching to a monotrophic diet can have a significant impact on your overall health. By consuming only one type of food at a time, you are allowing your digestive system to work more efficiently. This can lead to improved digestion and absorption of nutrients, which can have a positive effect on your overall well-being.
Furthermore, a monotrophic diet can help to regulate blood sugar levels, as it eliminates the consumption of processed and refined foods that are often high in sugar and unhealthy fats. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as it can help to manage their condition and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
In addition, following a monotrophic diet can lead to weight loss and improved metabolism. By focusing on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, you are providing your body with essential vitamins and minerals, which can support a healthy metabolism and promote weight loss.
Moreover, this diet can also have a positive impact on mental health. By consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other natural foods, you are providing your body with the nutrients it needs to function optimally, which can help to improve mood and mental clarity.
How to Transition to a Monotrophic Diet
How to Transition to a Monotrophic Diet
Transitioning to a monotrophic diet can be a significant change for your body, so it’s important to do so gradually and with the right approach. One key step in transitioning to a monotrophic diet is to start by incorporating more monofruits into your daily meals. These are fruits that consist of a single type, such as apples, bananas, or oranges. By gradually replacing some of your regular meals or snacks with monofruits, you can begin to adjust your body to the new eating pattern.
Another important aspect of transitioning to a monotrophic diet is to focus on eating fully ripe, fresh, and organic fruits. This ensures that you’re getting the most nutrients and benefits from the fruits you consume. Additionally, it’s important to pay attention to how your body responds to the new diet. Some people may experience changes in digestion, energy levels, or cravings as they transition to a monotrophic diet, so it’s crucial to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed.
As you make the transition, it’s also helpful to gradually eliminate processed foods, refined sugars, and other non-fruit items from your diet. This will help your body adjust to the new eating pattern and fully experience the benefits of a monotrophic diet. It’s important to note that every individual’s journey to a monotrophic diet will be unique, so be patient and kind with yourself throughout the transition process.
In summary, transitioning to a monotrophic diet involves gradually incorporating monofruits into your meals, focusing on ripe and organic fruits, paying attention to your body’s response, and gradually eliminating non-fruit items from your diet. By approaching the transition with patience and mindfulness, you can successfully shift to a monotrophic diet and experience its potential benefits.