Learn about the significance of kosher certification, permitted and prohibited foods, health benefits, and the dietary laws of kosher eating.
Understanding Kosher Dietary Laws
Contents
Kosher dietary laws are a set of guidelines and regulations that govern the types of food that can be consumed by individuals of the Jewish faith. These laws are based on the principles outlined in the Torah and are designed to promote physical and spiritual well-being. The dietary laws cover everything from the types of animals that can be eaten to the way in which food is prepared and served.
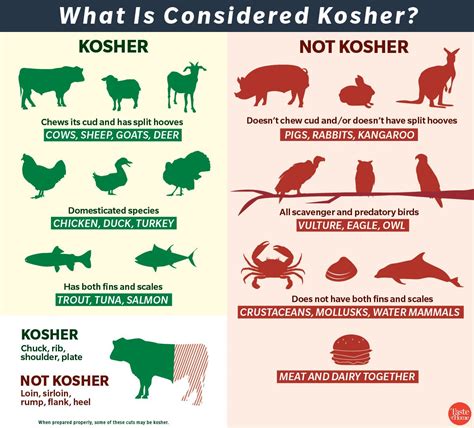
One of the key aspects of Kosher dietary laws is the prohibition of consuming certain types of animals. For example, the consumption of pork and shellfish is strictly forbidden, as these animals are considered unclean according to kosher standards. Additionally, meat and dairy products must never be consumed together, as this is seen as a violation of the principle of separating meat and milk.
Another important aspect of kosher dietary laws is the way in which food is prepared and served. For example, meat must be slaughtered in a specific, humane way known as Shechita, and certain parts of the animal, such as the sciatic nerve and certain types of fat, must be removed before consumption. Additionally, utensils used for preparing and serving food must be kept separate for meat and dairy products.
Overall, the Kosher dietary laws serve as a way for individuals of the Jewish faith to maintain a healthy and spiritually fulfilling lifestyle. By understanding and following these regulations, individuals can connect with their religious heritage and lead a life that is in accordance with their beliefs and values.
The Importance of Kosher Certification
Kosher certification is a critical aspect of the Kosher diet and holds great importance in the Jewish community. It ensures that the food products comply with the Kosher dietary laws and are suitable for consumption according to Jewish traditions. The certification is a guarantee for consumers that the food has been prepared, processed, and stored in accordance with the strict requirements of Kosher laws.
Obtaining Kosher certification involves various procedures such as thorough inspection of ingredients, packaging, and production facilities. This certification assures the consumers that the food has met the stringent standards set by Kosher laws and is free from any non-Kosher contaminants, additives, or ingredients.
Moreover, Kosher certification not only caters to the religious beliefs of the Jewish community but also enhances the marketability of food products. Many consumers, irrespective of their religious affiliations, seek out Kosher certified products due to the perceived quality, purity, and ethical standards associated with Kosher laws.
Additionally, obtaining a Kosher certification signifies a commitment to transparency and accountability in food production. It demonstrates the willingness of manufacturers and producers to adhere to specific standards and regulations, thereby building trust and credibility among consumers.
Foods Permitted in a Kosher Diet
In a Kosher diet, certain foods are permitted according to traditional Jewish dietary laws. These foods are classified as either meat or dairy and must meet specific guidelines for preparation and consumption.
Meat that is allowed in a Kosher diet includes beef, lamb, and poultry, as well as certain types of fish with scales and fins. These meats must be slaughtered and prepared in accordance with Kosher laws, which involve draining the blood and removing certain parts of the animal.
Dairy products permitted in a Kosher diet include those derived from Kosher animals, such as cow’s milk, goat’s milk, and sheep’s milk. These products must also be prepared and consumed in a manner that adheres to Kosher guidelines.
Fruits, vegetables, and grains are also permitted in a Kosher diet, provided that they are free from insects or other non-Kosher contaminants. However, there are specific guidelines for inspecting and preparing these foods to ensure they remain Kosher.
By following these guidelines for permitted foods in a Kosher diet, individuals can maintain a diet that aligns with their religious and cultural beliefs while also enjoying a wide variety of nutritious and flavorful options.
Prohibited Foods in Kosher Dietary Laws
One of the key aspects of following a Kosher diet is adhering to the prohibited foods in Kosher dietary laws. In order to maintain the sanctity of the diet, there are specific guidelines that outline the foods that are not permitted for consumption. These restrictions are based on the teachings of the Torah and have been followed by the Jewish community for centuries.
Some of the prohibited foods in a Kosher diet include any products derived from non-kosher animals, such as pork and shellfish. These animals do not meet the criteria set forth in Kosher dietary laws and are therefore considered unclean. Additionally, mixing meat and dairy products in the same meal is strictly prohibited, as it goes against the principle of separating milk and meat. This means no cheeseburgers or milk with a steak.
Furthermore, certain parts of permitted animals, such as the sciatic nerve and certain fats, are also prohibited according to Kosher dietary laws. This attention to detail is a testament to the dedication that adherents of the Kosher diet have towards following the guidelines set forth in their religious texts.
It is important to note that the prohibited foods in Kosher dietary laws extend beyond just the types of food that can be consumed. The way in which the food is prepared and processed also plays a significant role in whether or not it is considered Kosher. For example, utensils and cookware used to prepare non-Kosher foods must be kept separate from those used for Kosher meals. This level of adherence to Kosher dietary laws is essential for those who observe the diet as a way of maintaining their religious and cultural identity.
Health Benefits of a Kosher Diet
Health Benefits of a Kosher Diet
Health Benefits of a Kosher Diet
A Kosher diet is one that adheres to the dietary laws set forth in the Torah. These laws dictate not only what foods are permissible to eat, but also how those foods must be prepared and served. While the primary purpose of a Kosher diet is to adhere to religious beliefs, there are also several health benefits associated with this type of eating plan.
One of the main health benefits of a Kosher diet is the emphasis on cleanliness and food safety. The laws surrounding Kosher food preparation require certain hygiene standards to be met, including the thorough cleansing of meat and the separation of dairy and meat products. This focus on cleanliness can reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and contamination, leading to improved overall health.
In addition to the emphasis on cleanliness, a Kosher diet also promotes healthy eating habits. The restrictions on certain types of meat, such as pork, and the prohibition of mixing meat and dairy products can lead to a diet that is lower in saturated fats and cholesterol. This can have a positive impact on heart health and can contribute to a reduced risk of conditions such as heart disease and high blood pressure.
Furthermore, the Kosher diet emphasizes the importance of mindful eating. The laws surrounding the consumption of meat require animals to be slaughtered in a specific way, with an emphasis on minimizing pain and suffering. This can lead to a greater appreciation for the food being consumed and a more mindful approach to eating in general.
Overall, while the primary focus of a Kosher diet is rooted in religious tradition, there are numerous health benefits that can be gained from adhering to these dietary laws. From improved food safety to promoting healthier eating habits and mindfulness, a Kosher diet can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being.