Explore the fascinating history of the Two Sicilies Kingdom, from its origins and unification to the influence of the Bourbons and Napoleon’s impact. Witness the end of a powerful kingdom.
Origins of Two Sicilies
Contents
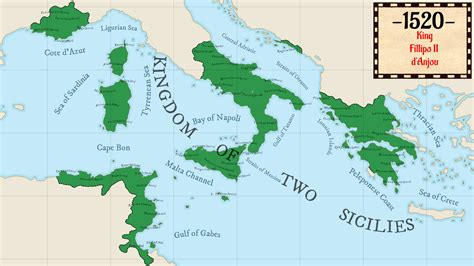
The Origins of Two Sicilies can be traced back to the ancient Greek colonization of the island of Sicily in the 8th century BC. This laid the foundation for the rich cultural and historical heritage of the region, which would eventually become a part of the Kingdom of Sicily. The merging of the Kingdom of Sicily and the Kingdom of Naples in 1816 solidified the creation of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, with the capital located in Naples.
Over the centuries, the region saw the influence of various civilizations, including the Greeks, Romans, Arabs, Normans, and Spanish, each leaving their mark on the cultural and architectural landscape of the Two Sicilies. The diverse and complex history of the region is reflected in its art, cuisine, and traditions, making it a captivating destination for history enthusiasts.
The unification of the two kingdoms under the House of Bourbon was a significant turning point in the history of the Two Sicilies, marking the beginning of a new era for the region. Under Bourbon rule, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies experienced periods of prosperity and development, as well as challenges and conflicts, shaping its identity and character.
Today, the legacy of the Bourbons can still be seen in the architectural marvels, such as the Royal Palace of Caserta and the Teatro San Carlo, that stand as a testament to their influence on the cultural landscape of the Two Sicilies. The artistic achievements and contributions of the Bourbon monarchs continue to be celebrated and appreciated in the region.
The origins of Two Sicilies are deeply intertwined with the tumultuous events of the Napoleonic era, which had a profound impact on the political and social dynamics of the region. The conquest of the Kingdom of Naples by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1806 led to the establishment of the Parthenopean Republic, altering the course of history for the Two Sicilies. The subsequent reconfiguration of the region under French influence left a lasting imprint on its governance and administration.
Unification of the Two Kingdoms
The unification of the Two Sicilies refers to the merging of the Kingdom of Sicily and the Kingdom of Naples in the early 19th century. This significant event in Italian history occurred in 1816 when the two kingdoms were united to form the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. This unification was the result of the Congress of Vienna, which aimed to reorganize the political map of Europe after the defeat of Napoleon.
The unification of the Two Sicilies was a complex process that involved diplomatic negotiations and political maneuvering. The Kingdom of Naples had been under French control during the Napoleonic Wars, while the Kingdom of Sicily had been under British protection. After the defeat of Napoleon, the two kingdoms were reorganized and merged into a single entity under the Bourbon dynasty.
The unification of the Two Sicilies had lasting implications for the newly formed kingdom. The merger of the two kingdoms brought together different political, social, and economic systems, leading to significant challenges in governance and administration. Additionally, the unification sparked resistance from various factions within the kingdom, leading to internal conflict and political instability.
Despite these challenges, the unification of the Two Sicilies marked an important milestone in Italian history. It set the stage for the emergence of a unified Italian state and laid the foundation for the Risorgimento, a period of intense nationalist activity that ultimately led to the unification of Italy in 1861.
Influence of the Bourbons
Influence of the Bourbons
The Bourbons had a significant impact on the history of the Two Sicilies Kingdom. The dynasty, which originated from France, ruled over the southern Italian region for centuries. Their rule brought about a blend of French and Italian cultural influences, shaping the identity of the region in a unique way.
One of the most notable legacies of the Bourbon influence was their contributions to the art and architecture of the Two Sicilies. The royal family patronized many artists, architects, and craftsmen, leading to the construction of grand palaces, churches, and public buildings. The Bourbon aesthetic style is still visible in the landmarks of Naples and other cities in southern Italy.
Moreover, the Bourbons also left a lasting impact on the economic and social structure of the Two Sicilies. Their policies and administrative reforms reshaped the region’s agricultural and industrial sectors, leading to significant changes in the livelihoods of the local populace. The Bourbon rule also saw the emergence of a distinct aristocratic class, further shaping the social hierarchy of the kingdom.
Furthermore, the Bourbons’ influence extended to the realm of education and intellectual life in the Two Sicilies. The royal court was a hub of cultural exchange and intellectual discourse, attracting prominent scholars and thinkers. The Bourbon rulers established universities and academies, fostering a rich tradition of scholarship and learning that endured for generations.
In summary, the influence of the Bourbons on the Two Sicilies was multi-faceted and enduring. Their legacy is still visible in the art, architecture, economy, and intellectual life of the region, making them a crucial part of its history and identity.
Napoleon’s Impact on Two Sicilies
During the early 19th century, Napoleon Bonaparte’s conquest of Europe had a significant impact on the Kingdom of Two Sicilies. As one of the most powerful and influential leaders of his time, Napoleon’s actions and policies had far-reaching consequences for the people of southern Italy and Sicily.
One of the most notable changes brought about by Napoleon’s rule was the introduction of the Napoleonic Code, a comprehensive system of laws that replaced the various legal traditions that had previously existed in the Kingdom of Two Sicilies. This new legal framework aimed to modernize the legal system and promote equality before the law, but it also brought about significant social and political changes.
In addition to legal reforms, Napoleon also implemented changes to the administrative and political structure of the Kingdom of Two Sicilies. He appointed his relatives and loyal supporters to key positions of power, consolidating his influence in the region and further integrating southern Italy and Sicily into his empire.
Furthermore, Napoleon’s impact on the economy of the Kingdom of Two Sicilies was profound. His policies aimed to stimulate economic growth and development, but they also resulted in increased taxation and economic hardship for many people in the region.
Overall, Napoleon’s influence on the Kingdom of Two Sicilies was complex and multifaceted, leaving a lasting legacy that shaped the region’s history and identity for years to come.
End of the Two Sicilies Kingdom
The Kingdom of Two Sicilies came to an end in 1861 as a result of the Italian unification movement. The unification of Italy, which aimed to consolidate various states and regions into one nation, had a significant impact on the Two Sicilies Kingdom. The end of the kingdom marked the culmination of a series of events that ultimately led to the establishment of a unified Italian state.
One of the key factors that contributed to the end of the Two Sicilies Kingdom was the Napoleonic Wars. The kingdom, ruled by the Bourbon dynasty, faced significant challenges as a result of the political and military upheaval brought about by Napoleon Bonaparte. The intrusion of French forces into the Italian peninsula disrupted the existing power structure and ultimately weakened the authority of the Bourbon kings in the Kingdom of Two Sicilies.
The influence of the Bourbons waned as the Italian unification movement gained momentum. The rise of nationalist sentiments and the desire for political unity among various Italian states posed a direct challenge to the pre-existing monarchies, including the Kingdom of Two Sicilies. The revolutionary fervor that swept across Italy in the 19th century ultimately led to the downfall of the Bourbon rulers and the disintegration of their kingdom.
The end of the Kingdom of Two Sicilies marked a significant turning point in Italian history. The unification of Italy under a single sovereign state had profound implications for the political, social, and cultural landscape of the Italian peninsula. The events that culminated in the end of the Two Sicilies Kingdom not only reshaped the map of Italy but also had far-reaching repercussions that reverberated throughout European geopolitics.