Explore the rich history of Switzerland, from ancient civilizations to the impact of the Roman Empire and French Revolutionary Wars. Discover the country’s journey through the Reformation and medieval confederacy.
Ancient Swiss Civilizations
Contents
When discussing the ancient history of Switzerland, it’s important to consider the various civilizations that inhabited the region. One of the earliest known groups were the Celtic tribes who settled in what is now modern-day Switzerland around the 5th century BC. These tribes were known for their advanced metalworking skills, as well as their intricate artwork and intricate religious beliefs.
Another significant ancient civilization in Switzerland was the Roman Empire, which conquered the region in the 1st century BC. The Romans established numerous settlements and roads throughout Switzerland, leaving behind a lasting impact on the culture and infrastructure of the area. The influence of the Roman Empire can still be seen in the architecture and language of modern-day Switzerland.
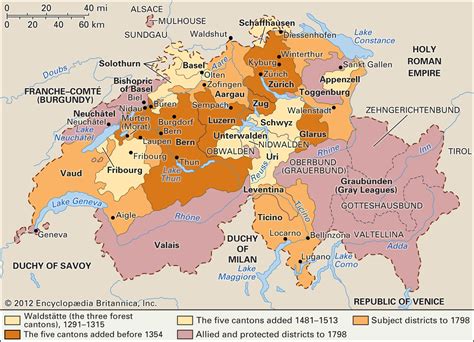
During the Medieval period, Switzerland was home to various feudal kingdoms and city-states, each with their own unique cultures and traditions. This diverse landscape laid the foundation for the modern-day Swiss Confederacy, which was formed in the 13th century as an alliance of independent states.
As the Reformation swept across Europe in the 16th century, Switzerland played a key role in the religious and political upheaval. The country became a battleground for competing religious ideologies, with the Protestant and Catholic factions vying for control. This tumultuous period shaped the religious landscape of Switzerland and led to the formation of the modern Swiss state.
Finally, the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century had a profound impact on Switzerland. The country was invaded by French forces, leading to the collapse of the Swiss Confederacy and the establishment of the Helvetic Republic. This period of upheaval ultimately paved the way for the modern Swiss federal state that we know today.
Influence of Roman Empire
The Roman Empire had a significant impact on the development of Switzerland, particularly in the areas of language, culture, and governance. The Romans established numerous settlements in the region, bringing with them their language, Latin, which would eventually evolve into the modern Swiss languages of French, German, Italian, and Romansh. This linguistic influence can still be seen today in the diverse linguistic landscape of Switzerland.
Additionally, the Roman system of governance and infrastructure also left a lasting mark on Switzerland. The Romans built roads, bridges, and fortifications, which helped to connect and protect their settlements. Many of these Roman-built structures are still in use today, and the layout of some modern Swiss cities still reflects the Roman grid pattern. The Roman Empire also introduced new agricultural techniques and products, such as grapes and wine, which continue to be important to the Swiss economy.
Furthermore, the Romans brought with them their cultural and religious practices, including the introduction of Christianity. The development of Christian communities and the construction of churches and monasteries had a lasting impact on the religious and cultural identity of Switzerland. The Roman legacy can be seen in the numerous Roman ruins and artifacts that have been unearthed throughout Switzerland, serving as a physical reminder of their influence on the region.
In summary, the influence of the Roman Empire on Switzerland was profound and far-reaching, shaping the linguistic, cultural, and governance aspects of the country. The legacy of the Romans continues to be an important part of Swiss history and identity.
Medieval Swiss Confederacy
The Medieval Swiss Confederacy refers to the period between the late 13th century and the early 16th century when the various cantons of Switzerland formed a loose alliance for mutual defense and cooperation. This period was marked by the rise of several independent cantons, such as Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden, which eventually joined forces to resist the expanding influence of external powers.
During the Medieval Swiss Confederacy, the cantons banded together to defend their territories and ensure their sovereignty. The most famous event from this period is the legendary oath of the Rütli, where the representatives of the three founding cantons swore to support each other in the struggle for independence.
As the cantons continued to grow and expand, the Confederacy evolved into a more formal alliance, with the establishment of the Old Swiss Confederacy in the 14th century. This laid the groundwork for the development of a decentralized federal state, with each canton retaining a high degree of autonomy.
The Medieval Swiss Confederacy was not without its internal conflicts and struggles for power, but it laid the foundation for the modern Swiss state. This period was characterized by a spirit of independence and resistance to external domination, which continues to be a defining feature of Swiss identity.
Switzerland in the Reformation
The Reformation in Switzerland was a significant period of religious and political change in the 16th century. It was a time of great upheaval as new religious ideas and movements swept across the country, challenging the traditional authority of the Roman Catholic Church and leading to the establishment of Protestant churches in various regions.
The Protestant Reformation was sparked in Switzerland by the teachings of Ulrich Zwingli, a priest and humanist scholar who criticized the doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church. Zwingli’s ideas gained traction in the city of Zurich and other urban centers, leading to the formation of a distinct Swiss Reformed tradition.
As the Reformation spread, it triggered conflict and division within Swiss society. The Swiss Confederation was comprised of regions with differing religious allegiances, leading to tensions and even armed conflicts between Catholic and Protestant cantons. This period of religious strife, known as the Wars of Kappel, represented a tumultuous chapter in Swiss history.
Despite the internal conflicts, the Reformation brought lasting changes to Swiss society. It led to the establishment of distinct regional Protestant churches, the adoption of new forms of worship and church governance, and the reorganization of social and political structures. The Reformation also had long-term implications for Switzerland’s relationship with neighboring countries and the broader European religious landscape.
French Revolutionary Wars Impact
Blog Post: French Revolutionary Wars Impact
FRENCH REVOLUTIONARY WARS IMPACT
The French Revolutionary Wars had a significant impact on Switzerland, reshaping the country’s political landscape and leading to major changes in its governance and society. The wars, which lasted from 1792 to 1802, were a series of conflicts between the new French Republic and various European powers, including Switzerland. These wars had a profound impact on Switzerland, marking the end of the Old Swiss Confederacy and laying the groundwork for the modern Swiss state.
One of the major consequences of the French Revolutionary Wars was the collapse of the Old Swiss Confederacy, which had been a loose alliance of independent cantons since the late Middle Ages. The French invasion of Switzerland in 1798 led to the formation of the Helvetic Republic, a centralized state based on the principles of the French Revolution. This brought an end to the old system of cantonal sovereignty and marked the beginning of a new era of political centralization in Switzerland.
Furthermore, the French Revolutionary Wars also brought about significant social and economic changes in Switzerland. The introduction of the Helvetic Republic brought with it new ideas of citizenship and equality, which had a lasting impact on Swiss society. Reforms were implemented to modernize the country’s legal and administrative systems, and efforts were made to promote economic development and trade.
The French Revolutionary Wars also had a lasting impact on Switzerland’s relationship with the rest of Europe. The rise of Napoleon Bonaparte and the establishment of the French Empire led to continued political instability in Switzerland, as the country became a battleground for competing European powers. The Congress of Vienna in 1815 sought to restore stability to the region and reestablish Switzerland as a neutral state, a status that has endured to the present day.
In conclusion, the French Revolutionary Wars had a profound and lasting impact on Switzerland, reshaping its political, social, and economic landscape. The collapse of the Old Swiss Confederacy, the introduction of the Helvetic Republic, and the subsequent efforts to restore stability and neutrality all contributed to the modernization and development of Switzerland as a nation.