Explore the history of Saudi Arabia, from early civilizations to modern developments and Vision 2030. Learn about the rise of Islam and the Prophet Muhammad.
Early Civilizations in Arabian Peninsula
Contents
Early Civilizations in Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula has been home to some of the oldest civilizations in the world. It is an area rich in history and culture, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Bronze Age. The development of early civilizations in the region was influenced by its strategic location between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, as well as its abundance of natural resources.
One of the most well-known early civilizations in the Arabian Peninsula is the Kingdom of Ma’in, which thrived in the southern region of present-day Saudi Arabia around 1200 BCE. The Ma’inites were skilled in trade and agriculture, and their prosperity was built on the export of incense and other luxury goods to neighboring empires such as the Roman Empire.
Another significant civilization in the region was the Nabateans, who established a network of trade routes and impressive stone carvings in the area of present-day Jordan and northern Saudi Arabia. Their capital city of Petra became a thriving center of commerce and culture, attracting traders and travelers from far and wide.
The Arabian Peninsula was also home to the Sabaeans, who built the Kingdom of Saba in the southwestern region, known for its irrigation systems and agricultural terracing. The wealth and power of the Sabaeans were closely tied to their ability to control water resources and establish trade connections with other civilizations in the near East.
| Early Civilizations | Location | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom of Ma’in | Southern Saudi Arabia | Skilled in trade and agriculture, export of incense |
| Nabateans | Jordan and northern Saudi Arabia | Established trade routes and impressive stone carvings |
| Sabaeans | Southwestern Saudi Arabia | Developed irrigation systems and agricultural terracing |
These early civilizations laid the foundation for the rich cultural heritage of the Arabian Peninsula and left behind a legacy of impressive archaeological sites and historical artifacts. Their achievements in trade, agriculture, and architecture demonstrate the advanced level of development that existed in the region long before the rise of Islam.
Rise of Islam and the Prophet Muhammad
The Rise of Islam marks a crucial turning point in the history of the Arabian Peninsula. The Prophet Muhammad, born in Mecca in 570 AD, became the messenger of Islam after receiving revelations from the Angel Gabriel. His teachings and the subsequent spread of Islam had a profound impact on the region, shaping its religious, cultural, and political landscape.
As Muhammad’s following grew, the ruling elite in Mecca, who felt threatened by his message, eventually forced him and his followers to migrate to Medina in 622 AD. This event, known as the Hijra, is considered the starting point of the Islamic calendar and represents the shift of power and authority from the pagans to the Muslims.
Over the next decade, Muhammad’s influence expanded as he consolidated his power in Medina and eventually returned to Mecca, triumphantly establishing Islam as the prevailing religion of the region. His death in 632 AD marked the end of his leadership but set the stage for the Caliphates to continue spreading Islam across the Arabian Peninsula and beyond.
| Key Events | Significance |
|---|---|
| Revelations to Muhammad | Foundation of Islam |
| The Hijra | Shift of Power |
| Return to Mecca | Establishment of Islam |
The Rise of Islam and the Prophet Muhammad not only transformed the Arabian Peninsula but also had far-reaching effects on global history, influencing the development of religious, cultural, and political institutions for centuries to come.
Foundation of the First Saudi State
Foundation of the First Saudi State
The foundation of the First Saudi State dates back to the late 18th century, when Muhammad ibn Saud, a tribal leader, and Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab, a religious reformer, formed an alliance. This alliance between the Al Saud family and the Wahhabi religious movement laid the groundwork for the establishment of the First Saudi State. The ideology of the Wahhabi movement, which emphasized strict adherence to Islamic law, provided the political and religious underpinnings of the state.
Under the leadership of Muhammad ibn Saud and his descendants, the First Saudi State expanded its influence and controlled large parts of the Arabian Peninsula. The state prospered as it gained control over key trade routes and cities, allowing it to accumulate wealth and power. However, the state faced opposition from the Ottoman Empire, which sought to maintain its control over the region.
The First Saudi State reached its peak in the early 19th century, but it eventually faced internal and external challenges. In 1818, the Ottoman forces, supported by local tribes, launched a campaign to defeat the First Saudi State. This marked the end of the First Saudi State as it was destroyed and its territories were annexed by the Ottoman Empire.
The legacy of the First Saudi State, however, lived on as the descendants of Muhammad ibn Saud continued to resist Ottoman rule and eventually established the Second Saudi State in the 19th century. The foundation of the First Saudi State laid the groundwork for the formation of modern Saudi Arabia, as it marked the beginning of the political and religious alliance between the Al Saud family and the Wahhabi movement.
Formation of Modern Saudi Arabia
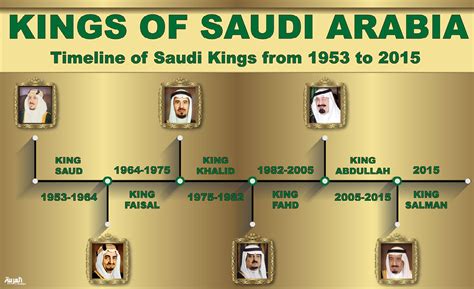
The formation of Modern Saudi Arabia started in the early 20th century, with the unification efforts of Abdulaziz Ibn Saud. After a series of battles and conquests, he succeeded in creating the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932, with himself as the first king. This marked the beginning of a new era for the region, as it transitioned from fragmented, tribal societies to a unified nation-state.
Under King Abdulaziz, the country experienced rapid modernization and development. He invested in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, and sought to create a strong, centralized government. His efforts laid the groundwork for the modernization of Saudi Arabia, setting the stage for the oil boom that would transform the country’s economy.
The discovery of oil in the 1930s proved to be a major turning point in the formation of Modern Saudi Arabia. The country quickly became one of the world’s leading oil producers, and the newfound wealth allowed for further investment in infrastructure and social programs. This period of economic growth and prosperity brought about significant changes in the country, as traditional ways of life gave way to a more modern and urban society.
Throughout the latter half of the 20th century, Saudi Arabia continued to modernize and develop, using its oil wealth to build a diverse economy and establish itself as a regional power. The country’s strategic position in the Middle East and its influence in the Islamic world further solidified its place on the global stage. This continued modernization and development have shaped Saudi Arabia into the modern and dynamic nation it is today.
Recent Developments and Vision 2030
The recent developments in Saudi Arabia have been nothing short of remarkable. With the introduction of Vision 2030, the country has been undergoing a massive transformation in various sectors. One of the key focus areas of Vision 2030 is economic diversification, with the aim of reducing the country’s dependency on oil. This has led to the development of various industries such as tourism, entertainment, and technology, which were previously untapped in the region.
Another important aspect of Vision 2030 is social and cultural development. The government has been actively working towards empowering the youth and women, and promoting a more open and tolerant society. Initiatives such as the lifting of the ban on women driving and the opening of cinemas and entertainment venues have been groundbreaking in the conservative society of Saudi Arabia.
In addition to this, the country has been making significant strides in the field of renewable energy. With the establishment of the King Salman Renewable Energy Initiative, Saudi Arabia aims to increase its renewable energy capacity to 27.3 gigawatts by 2024. This not only emphasizes the country’s commitment to sustainable development but also positions it as a leader in the global renewable energy market.
Furthermore, Saudi Arabia has been strengthening its relations with the international community through initiatives like the Saudi Green Initiative and the Middle East Green Initiative. These efforts reflect the country’s commitment to environmental conservation and sustainable development on a global scale.
Overall, the recent developments in Saudi Arabia, coupled with the ambitious goals of Vision 2030, indicate a promising future for the country. The transformation underway is not only reshaping the economic and social landscape of Saudi Arabia but also positioning it as a key player in the global arena.