Discover the formation, impact, challenges, expansion, and dissolution of the North German Union. Learn about its political and economic influence.
Formation of North German Union
Contents
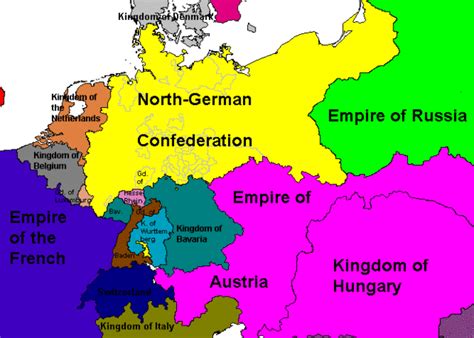
The formation of the North German Union was a significant turning point in the history of Europe. It took place in 1867, following the Austro-Prussian War, which resulted in the defeat of Austria and the exclusion of Austria from German affairs. This allowed Prussia to take the lead in the unification of Germany and to create the North German Union.
At the forefront of this formation was Otto von Bismarck, the Chancellor of Prussia, who skillfully used diplomacy and military strategies to achieve his goal of unifying the German states under Prussian leadership. Bismarck’s success in the formation of the North German Union laid the groundwork for the eventual creation of the German Empire in 1871.
The formation of the North German Union had both political and economic implications. Politically, it shifted the balance of power in Europe and established Prussia as the dominant force in German politics. Economically, it provided a unified market for trade and commerce, leading to increased industrialization and economic prosperity.
The formation of the North German Union was not without its challenges and opposition. There were internal tensions among the German states, particularly with regards to the role of Austria and the southern states. Additionally, there was resistance from other European powers, such as France, who viewed the growing power of Prussia with suspicion.
Political and Economic Impact
The Formation of the North German Union had significant political and economic impact not only in the region but also in the larger European context. With the unification of the German states under the leadership of Prussia, there was a shift in the balance of power in Europe. This new union posed a challenge to the existing European powers, particularly Austria and France, as it solidified Germany’s position as a major player on the continent.
From an economic standpoint, the North German Union facilitated greater trade and commerce within its borders. The implementation of a common currency, the North German Thaler, and the removal of internal tariffs resulted in increased economic integration and growth. This economic impact was felt not only within the union but also in its trade relations with neighboring countries, reinforcing Germany’s position as an economic powerhouse in Europe.
On the political front, the North German Union ushered in a new era of diplomacy and alliances. As the union consolidated its power, it began to form alliances with other European nations, further solidifying its standings on the international stage. This shift in alliances and power dynamics had a ripple effect across the continent, shaping the course of European politics for years to come.
The political and economic impact of the North German Union cannot be overstated. Its formation led to a reconfiguration of power dynamics in Europe and greatly influenced the economic landscape of the region. The union’s rise to prominence brought about a new era of diplomacy and trade relations that resonated far beyond its borders, leaving a lasting impact on the continent.
Challenges and Opposition
The formation of the North German Union faced a myriad of challenges and opposition from various fronts. One of the primary challenges was the resistance from the southern German states, particularly Austria, which felt threatened by the growing power of Prussia in the region. Additionally, internal opposition within the Prussian government and among the people also posed significant challenges to the formation of the Union. The unification process faced opposition from conservative forces who were apprehensive about the potential changes that would come with a unified Germany.
Furthermore, the economic challenges that accompanied the formation of the Union cannot be overlooked. The integration of the different economies of the member states posed significant challenges as it required the harmonization of laws, regulations, and economic policies. Economic disparities between the member states also created hurdles in the formation of a common economic framework. The opposition from various social and economic groups, who feared loss of autonomy and economic control, further compounded the challenges faced by the North German Union.
In addition, the ideological opposition to the formation of the Union also played a significant role. The ideas of nationalism and German identity were not universally accepted, and many individuals and groups were resistant to the idea of a unified Germany. Political opposition also arose from neighboring countries and other European powers who were concerned about the implications of a united and powerful Germany. The complexities of addressing these multifaceted challenges and overcoming the various forms of opposition required strategic and diplomatic maneuvering on the part of the proponents of the North German Union.
In conclusion, the challenges and opposition faced during the formation of the North German Union were diverse and multifaceted, encompassing political, economic, social, and ideological dimensions. Overcoming these hurdles required resilience, negotiation, and compromise, and the eventual formation of the Union marked a significant milestone in the history of Germany and Europe.
Expansion and Integration
The Expansion and Integration of the North German Union was a pivotal turning point in the history of Europe in the 19th century. After its formation in 1867, the North German Union sought to expand its influence and integrate various states and territories into its fold. This process was marked not only by political maneuvering and diplomatic efforts, but also by economic incentives and the promise of stability and security for the regions that chose to join.
One of the key strategies employed during the Expansion and Integration phase was the establishment of trade agreements and economic partnerships with neighboring states. The North German Union aimed to create a network of interconnected economies that would benefit from shared resources, increased market access, and mutually beneficial trade arrangements.
As part of its integration efforts, the North German Union also worked to standardize laws, regulations, and administrative structures across the territories under its influence. This harmonization of governance systems was designed to streamline processes, promote cooperation, and facilitate the smooth functioning of the newly integrated regions.
The expansion and integration of the North German Union was not without its challenges, as resistance and opposition from some quarters posed significant obstacles. However, through a combination of political negotiation, economic incentives, and strategic alliances, the union was able to overcome many of these challenges and successfully expand its reach and influence.
Ultimately, the expansion and integration of the North German Union reshaped the political and economic landscape of Europe, laying the groundwork for a new era of cooperation and collaboration among the member states. The union’s commitment to integration and expansion set the stage for a period of unprecedented growth and prosperity for the region as a whole.
Dissolution of North German Union
The Dissolution of the North German Union marked the end of a period of political and economic integration in northern Germany. The union, which was formed in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War, brought together a number of German states under the leadership of Prussia. However, as time passed, internal divisions and external pressures led to the dissolution of this once-powerful alliance.
One of the main factors contributing to the dissolution of the North German Union was the rise of internal opposition. As the union expanded, smaller states within the alliance began to assert their desire for greater autonomy. This push for independence created tension within the union and ultimately weakened its cohesiveness. Additionally, external powers, such as France, sought to exploit these internal divisions to undermine the unity of the union.
Furthermore, economic challenges also played a significant role in the dissolution of the North German Union. The economic disparities between the various states within the union created friction and hindered efforts to maintain a unified economic policy. This lack of economic cohesion further undermined the stability of the alliance and contributed to its eventual demise.
Despite attempts to address these challenges, the dissolution of the North German Union became inevitable. The inability to overcome internal divisions and economic disparities ultimately led to the unraveling of this once-powerful political and economic alliance.