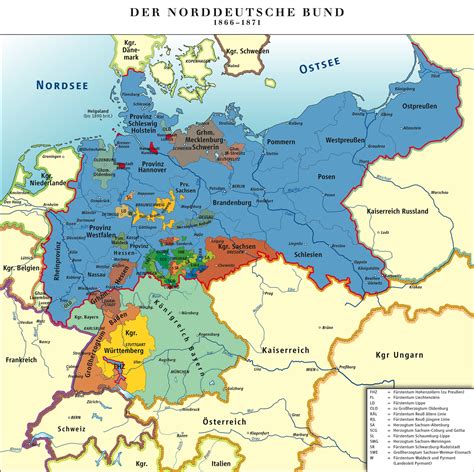
Explore the formation, unification, and fall of the North German Confederation, and its impact on politics, military, constitution, economy, and industrialization.
Formation of North German Confederation
Contents
The Formation of North German Confederation was a pivotal moment in the history of Germany, marking the beginning of political and military unification in the region. Following the successful conclusion of the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, Bismarck and the Prussian government took the opportunity to consolidate their power by creating a confederation of northern German states. This move was seen as a strategic step towards achieving the larger goal of unifying all German-speaking states under Prussian leadership.
One of the key aspects of the formation of the North German Confederation was the debate on its constitution. Bismarck and his allies worked tirelessly to draft a constitution that would ensure the centralization of power in the hands of the Prussian monarchy, while also allowing for a degree of representation from the constituent states. The resulting constitution established a federal system with a strong executive, paving the way for a more unified and centralized German state.
The economic growth and industrialization that accompanied the formation of the North German Confederation further solidified its place on the world stage. By promoting free trade and economic cooperation among member states, the confederation was able to stimulate rapid industrial development and economic expansion. This period of growth laid the groundwork for the economic powerhouse that Germany would become in the decades to come.
The Formation of North German Confederation was not without its challenges, and the eventual fall of the confederation marked the end of an era. However, its impact on the history of Germany cannot be understated, as it set the stage for the eventual unification of all German states under a single national government.
Political and Military Unification
The Political and Military Unification of the North German Confederation was a pivotal moment in the history of Germany. After years of fragmentation and disunity, the various German states sought to come together to form a more cohesive and powerful nation. This process of unification was characterized by both political negotiations and military conflicts, as different states vied for control and influence.
One of the key figures in this Political and Military Unification was Otto von Bismarck, the Minister President of Prussia. Bismarck skillfully maneuvered through the complex web of alliances and rivalries to bring about the unification of the German states under Prussian leadership. Through a series of carefully orchestrated wars and diplomatic negotiations, Bismarck was able to achieve his goal of creating a united German nation.
However, the process of Political and Military Unification was not without its challenges and opposition. Many of the smaller states resisted Prussian dominance, and there were widespread debates and disagreements over the terms of unification. Additionally, the military conflicts that were waged as part of this process resulted in loss of life and destruction.
Despite these difficulties, the Political and Military Unification of the North German Confederation ultimately succeeded in creating a single, unified German state. This newfound unity would lay the groundwork for the later formation of the German Empire, and would have a lasting impact on the course of European history.
Debate on Constitution
The debate on the constitution of the North German Confederation was a crucial moment in the history of the newly formed state. After the successful military and political unification of the northern German states, the question of the constitutional framework became a topic of intense discussion among the political leaders and representatives.
The main issue at hand was the balance of power between the federal government and the individual states. Some argued for a strong, centralized government with extensive powers, while others advocated for a more decentralized system with greater autonomy for the member states. This debate was reflective of the broader tensions between nationalism and federalism that characterized the political landscape of the time.
Ultimately, a compromise was reached with the adoption of the constitution of the North German Confederation in 1867. This document established a federal state with a bicameral legislature, a president, and a chancellor. The division of powers between the federal and state governments was carefully delineated, and measures were put in place to protect the rights and autonomy of the individual states while also ensuring the unity and stability of the confederation as a whole.
The debate on the constitution not only shaped the political structure of the North German Confederation but also set the stage for the subsequent formation of the German Empire. The compromises and agreements reached during this period laid the groundwork for the future development of Germany as a unified and powerful nation in the heart of Europe.
Economic Growth and Industrialization
The economic growth of the North German Confederation during the late 19th century was a result of industrialization and modernization. The expansion of the railroad network and the adoption of new technologies played a crucial role in the development of the economy. This period saw a shift from agrarian to industrial production, with the rise of industries such as textiles, steel, and coal mining.
Furthermore, the government’s support for economic development through policies such as tariffs and subsidies for domestic industries contributed to the overall growth of the economy. This support created a favorable environment for entrepreneurs and investors, leading to an increase in production and exports.
The industrialization of the North German Confederation also led to urbanization, as people moved from rural areas to cities in search of employment opportunities in factories and workshops. This shift in population distribution further fueled the growth of urban economies and the development of infrastructure such as housing, transportation, and utilities.
During this period, the North German Confederation became a major player in the global economy, with its industrial products being exported to markets around the world. The increase in trade and commerce brought about prosperity and wealth, leading to the emergence of a middle class and consumer culture.
Fall of the North German Confederation
The North German Confederation came to an end in 1871 following the German Unification Wars, also known as the Franco-Prussian War. This conflict between France and Prussia resulted in the defeat of France and the formation of the German Empire, which replaced the Confederation. The fall of the North German Confederation marked a significant shift in power and influence in Europe, as the new German Empire emerged as a dominant force on the continent.
One of the key factors that led to the fall of the Confederation was the ambitions of Prussia’s leader, Otto von Bismarck. Bismarck’s goal was to unify the German states under Prussian leadership, and the defeat of France in the war helped to achieve this objective. The success of Prussia in the conflict bolstered Bismarck’s position and paved the way for the establishment of the German Empire, marking the end of the confederation.
The fall of the North German Confederation also had significant consequences for the balance of power in Europe. The emergence of the German Empire as a major player on the European stage changed the dynamics of international relations and had a lasting impact on the continent. The fall of the confederation signaled the beginning of a new era in European history, with Germany asserting its influence and challenging the existing power structures.
In addition to the political and military implications, the fall of the North German Confederation also had economic repercussions. The rise of the German Empire as an industrial and economic powerhouse transformed the economic landscape of Europe and contributed to the continent’s industrialization. The fall of the Confederation was a pivotal moment in European history, shaping the future of the region in numerous ways.
Overall, the fall of the North German Confederation was a watershed moment in European history, marking the end of one era and the beginning of another. The emergence of the German Empire as a dominant force reshaped the political, military, and economic landscape of Europe, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to be felt to this day.