Explore the early settlements, Viking age expansion, formation of a kingdom, Hanseatic League influence, and union with Norway and Sweden in this informative blog post.
Early Settlements
Contents
History of Denmark
Denmark has a rich history that dates back to the early settlements of the prehistoric era. The first evidence of human presence in Denmark dates back to the Paleolithic period, with early hunter-gatherer communities inhabiting the land. These early settlers were drawn to the region due to its fertile land and abundant natural resources, which provided a suitable environment for sustenance and community development. As time progressed, these early settlements evolved into sophisticated societies, laying the foundation for the future growth and development of Denmark.
During the Neolithic period, agriculture and farming techniques became more prevalent in Denmark, allowing for the establishment of more permanent settlements. This marked a significant shift in the way of life for the inhabitants, as they transitioned from a nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a more settled and agricultural-based society. The introduction of farming technologies and domesticated animals allowed for the population to grow and communities to thrive.
As the early settlements of Denmark continued to expand and develop, the introduction of bronze and iron tools and weapons further advanced the capabilities and productivity of the inhabitants. This period saw the construction of impressive burial mounds and archaeological sites, indicative of the growing sophistication and cultural significance of the early Danish settlements.
The early settlements of Denmark played a critical role in shaping the cultural, social, and economic landscape of the region. The foundations laid by these early communities laid the groundwork for the subsequent historical events that would shape Denmark into the nation it is today. The legacy of the early settlements is still evident in the rich cultural heritage and historical significance of Denmark.
Viking Age Expansion
The Viking Age Expansion was a period of great exploration and conquest for the people of Denmark. During this time, the Vikings, also known as the Norsemen, ventured out from their homeland and traveled far and wide, reaching as far as the Mediterranean Sea, North Africa, and even North America. They were skilled sailors and navigators, using their longships to travel across the open sea and establish new settlements in foreign lands.
These intrepid explorers did not simply plunder and pillage, however. They also established trade routes and formed alliances with other nations, bringing back valuable goods and knowledge to their homeland. Their expeditions not only brought wealth and prestige to Denmark, but also expanded their influence across Europe and beyond.
The impact of the Viking Age Expansion was profound, leaving a lasting mark on the history and culture of Denmark and the regions they visited. Their legacy can be seen in the language, traditions, and even the genetic makeup of modern-day Scandinavians. The Vikings were pioneers of their time, paving the way for future exploration and colonization, and their adventurous spirit continues to inspire people to this day.
Formation of a Kingdom
Denmark’s formation as a kingdom is an interesting chapter in its history, marked by significant developments and power struggles. During the Viking Age, Denmark was divided into smaller clans and tribes, each ruling their own territories. However, in the 10th century, the kingdom began to take shape under the rule of Gorm the Old, who is considered the first historical Danish king.
Under the leadership of Gorm the Old and his son Harald Bluetooth, Denmark saw the consolidation of power and the formation of a unified kingdom. It was during Harald Bluetooth’s reign that Christianity was officially introduced, marking a major turning point in Denmark’s history.
By the 11th century, Denmark had firmly established itself as a kingdom, with a strong central government and a clear sense of national identity. The kingdom continued to grow in influence, expanding its territory and forging alliances with neighboring kingdoms.
One of the most significant events in the formation of Denmark as a kingdom was the reign of Canute the Great, who not only ruled over Denmark, but also united England, Norway, and parts of Sweden under his rule. This period of expansion and consolidation further solidified Denmark’s status as a major power in Northern Europe.
Hanseatic League Influence
During the late medieval period, the Hanseatic League played a significant role in the history of Denmark. The league, a commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and their market towns, had a major influence on the economy and trade of Denmark. Danish kings granted the league certain privileges, allowing them to establish trading posts and warehouses in major Danish cities such as Copenhagen and Helsingør.
The influence of the Hanseatic League in Denmark was particularly evident in the city of Lübeck, which served as the headquarters of the league. Lübeck became a key hub for trade between Denmark and other Hanseatic cities, facilitating the exchange of goods such as herring, grain, and timber. The league’s economic power and extensive network of trade routes contributed to the growth and prosperity of Danish urban centers during this period.
In addition to its economic impact, the Hanseatic League also held significant political influence in Denmark. The league’s merchants and representatives wielded considerable power in the Danish royal court, often participating in the decision-making process and shaping trade policies. This close relationship between the league and Danish rulers further solidified the league’s presence in the country.
Furthermore, the Hanseatic League’s influence extended beyond trade and politics, leaving a lasting cultural legacy in Denmark. The league’s members brought new ideas, customs, and technologies to Danish society, contributing to the enrichment and diversification of the country’s cultural landscape. The architectural style of Hanseatic buildings, for example, influenced the design and construction of structures in Danish cities.
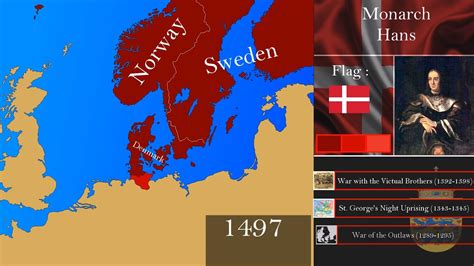
Union with Norway and Sweden
In 1397, Denmark entered into a union with Norway and Sweden, known as the Kalmar Union. This union was a political move to unite the three countries under a single monarch, with the aim of establishing peace and stability in the region. The union was formed through the Treaty of Kalmar, which was signed by the rulers of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. Under the terms of the union, each country retained its own laws and customs, but all three were ruled by a single monarch.
The union was initially successful in achieving its goal of peace and stability, but tensions soon began to emerge between the three countries. Denmark, being the dominant partner, often tried to assert its authority over Norway and Sweden, leading to resentment and conflict. In 1523, Sweden broke away from the union and established its own independent monarchy, effectively dissolving the Kalmar Union.
Despite the eventual dissolution of the union, the period of union with Norway and Sweden had a significant impact on the history of Denmark. It marked a time of cultural exchange and cooperation between the three countries, as well as a period of conflict and rivalry. The legacy of the Kalmar Union continues to influence the relations between Denmark, Norway, and Sweden to this day.